The journey to a treatment for hereditary spastic paraplegia
In 2016, Darius Ebrahimi-Fakhari, MD, PhD, then a neurology fellow at Boston Children’s Hospital, met two little girls with spasticity and decreased muscle tone in their legs, which affected their walking. Both girls, Robbie Edwards and Molly Duffy, had been diagnosed with hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP), which comprises a group of more than 80 genetic ... Read More about The journey to a treatment for hereditary spastic paraplegia
A toast to BRD4: How acidity changes the immune response
It started with wine. Or more precisely, a conversation about it. “My colleagues and I were talking about how some people think drinking wine may be anti-inflammatory,” recalls Xu Zhou, PhD, from the Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition at Boston Children’s Hospital. “There’s no scientific ground for that, but we know wine is acidic.” ... Read More about A toast to BRD4: How acidity changes the immune response
A safe, pain-specific anesthetic shows preclinical promise
All current local anesthetics block sensory signals — pain — but they also interrupt motor signals, which can be problematic. For example, too much epidural anesthesia can prevent mothers in labor from being able to push. Prolonged local anesthesia after orthopedic surgery can leave patients unable to participate in rehab. Researchers at Boston Children’s Hospital ... Read More about A safe, pain-specific anesthetic shows preclinical promise
A unique marker for pericytes could help forge a new path for pulmonary hypertension care
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare condition that’s difficult to treat. The hallmarks of the disease — narrowing of the arterioles and capillaries that deliver blood to the lungs — force the heart to work harder. In severe cases, PAH can lead to heart failure. Pericytes support capillary function and may play a role ... Read More about A unique marker for pericytes could help forge a new path for pulmonary hypertension care
New research shows caregiver instability affects development
According to some estimates, more than 100 million children around the world experience separations from their caregiver every year. Previous research — much of it derived from the long-running Bucharest Early Intervention Project (BEIP), which followed Romanian orphans from infancy to age 22 — suggests that caregiver disruptions like separations or changes in placement can ... Read More about New research shows caregiver instability affects development
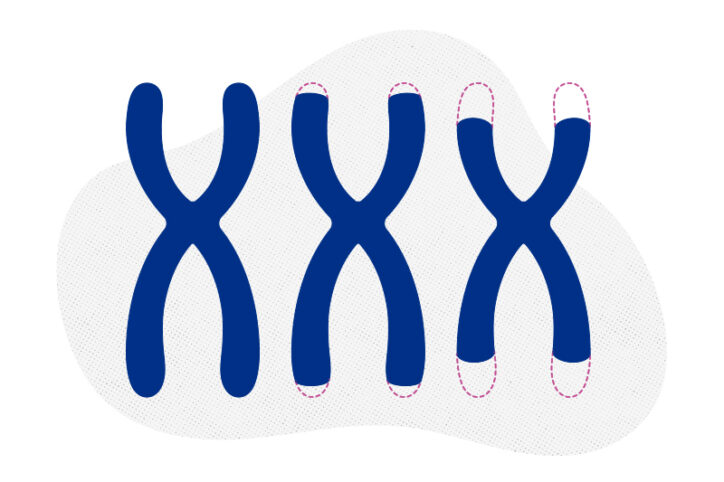
New research paves the way to a better understanding of telomeres
Much the way the caps on the ends of a shoelace prevent it from fraying, telomeres — regions of repetitive DNA sequences and a protein structure — protect the tips of chromosomes from damage. Every time our cells divide, telomeres lose a bit of that DNA. Eventually, telomeres become so short that they can no ... Read More about New research paves the way to a better understanding of telomeres